Introduction to Blood Cancer
- Introduction to Blood Cancer
- Definition and Types
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetic Factors
- Environmental Factors
- Other Risk Factors
- Symptoms and Signs
- General Symptoms
- Specific Symptoms Based on Type
- Diagnosis
- Blood Tests
- Biopsy
- Imaging Tests
- Treatment Options
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Stem Cell Transplant
- Immunotherapy
- Managing Side Effects
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Hair Loss
- Prognosis and Survival Rates
- Factors Affecting Prognosis
- Survival Rates for Different Types
- Support and Coping Strategies
- Support Groups
- Counseling
- Lifestyle Changes
- Research and Innovations
- Targeted Therapies
- Clinical Trials
- Prevention Strategies
- Lifestyle Changes
- Genetic Counseling
- Impact on Daily Life
- Physical Impact
- Emotional Impact
- Stories of Survival
- Personal Experiences
- Future Outlook
- Advances in Treatment
- Hope for Cure
- Conclusion
- FAQs
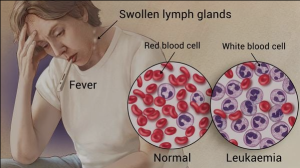
Introduction to Blood Cancer
Blood cancer, also known as hematologic cancer, originates in the blood-forming tissues or cells. There are three main types of blood cancers: leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma. These cancers affect the production and function of blood cells, leading to various symptoms and complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
Some blood cancers have a genetic component, meaning they can run in families. Certain genetic mutations increase the risk of developing blood cancer.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene and radiation, can increase the risk of developing blood cancer. Additionally, viral infections like Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) have been linked to certain types of blood cancer.
Other Risk Factors
Other risk factors include age, with older adults being at higher risk, as well as a weakened immune system due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or organ transplantation.
Symptoms and Signs
General Symptoms
Common symptoms of blood cancer include fatigue, unexplained weight loss, fever, and frequent infections. These symptoms can often mimic other illnesses, making diagnosis challenging.
Specific Symptoms Based on Type
Different types of blood cancer may present with specific symptoms. For example, leukemia may cause easy bruising and bleeding, while lymphoma can lead to swollen lymph nodes and night sweats.
Diagnosis
Blood Tests
Blood tests, such as complete blood count (CBC) and blood smear, are often the first step in diagnosing blood cancer. These tests can reveal abnormalities in the number and function of blood cells.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves taking a sample of tissue or cells from the affected area for examination under a microscope. This helps confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the type and severity of the disease.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests like CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans may be used to assess the extent of the disease and detect any spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment Options
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It is often used as the first-line treatment for many types of blood cancer.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Stem Cell Transplant
A stem cell transplant, also known as a bone marrow transplant, involves replacing diseased or damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells. This procedure can help restore the body’s ability to produce healthy blood cells.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy works by boosting the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It has shown promising results in treating certain types of blood cancer.
Managing Side Effects
Nausea and Vomiting
Medications can help control nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy and other treatments.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common side effect of blood cancer and its treatments. Patients are encouraged to rest and conserve energy while staying physically active when possible.
Hair Loss
Hair loss may occur with certain chemotherapy drugs. Wearing hats, scarves, or wigs can help manage this side effect.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Factors Affecting Prognosis
The prognosis for blood cancer depends on various factors, including the type and stage of the disease, the patient’s age and overall health, and the response to treatment.
Survival Rates for Different Types
Survival rates vary depending on the type of blood cancer. Some types, such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children, have high survival rates, while others, like certain types of myeloma, may have lower survival rates.
Support and Coping Strategies
Support Groups
Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice for patients and their families coping with blood cancer.
Counseling
Individual or family counseling can help patients and their loved ones navigate the challenges of living with blood cancer and its treatments.
Lifestyle Changes
Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can help improve overall well-being during cancer treatment.
Research and Innovations
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies are drugs that specifically target cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. They are a promising area of research for treating blood cancer.
Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can give patients access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to advancements in the field of blood cancer research.
Prevention Strategies
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of developing blood cancer.
Genetic Counseling
Individuals with a family history of blood cancer or certain genetic mutations may benefit from genetic counseling to assess their risk and explore preventive measures.
Impact on Daily Life
Physical Impact
Blood cancer and its treatments can have various physical effects, such as fatigue, pain, and changes in appetite. Patients may need to adjust their daily routines and activities accordingly.
Emotional Impact
Living with blood cancer can take a toll on mental health, leading to feelings of anxiety, depression, and uncertainty about the future. Seeking support from loved ones and mental health professionals can help address these emotional challenges.
Stories of Survival
Personal Experiences
Sharing stories of survival and resilience can inspire hope and provide encouragement to others facing a diagnosis of blood cancer. Hearing about successful treatment outcomes and life after cancer can offer reassurance and motivation.
Future Outlook
Advances in Treatment
Ongoing research and advances in treatment offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for patients with blood cancer. Scientists are exploring new therapies and treatment approaches to better target cancer cells and minimize side effects.
Hope for Cure
While blood cancer can be a challenging disease to treat, there is optimism about finding a cure through continued research and innovation